Understand if your compound is metabolized by aldehyde oxidase (AO).
Aldehyde oxidase (AO) reaction phenotyping is a non-CYP mediated metabolism assay within our portfolio of in vitro ADME screening services. Cyprotex delivers consistent, high quality data with the flexibility to adapt protocols based on specific customer requirements.
Introduction
Determining potential metabolism by aldehyde oxidase enzymes:
- Aldehyde oxidase is a cytosolic enzyme and is a sub family of the molybdo-flavoenzymes.
- For catalytic activity, aldehyde oxidase requires a molybdo-pterin cofactor (molybdenum cofactor, MoCo) and flavin adenine dinucleotide.
- It has broad substrate specificity and catalyses the oxidation of aldehydes into carboxylic acids and also thehydroxylation of some N-heterocycles.
- The main isoform in humans is AO1 which has highest activity in the liver. The enzyme has also been detected in other tissues such as the lung, gastrointestinal tract and kidney.
- Cyprotex’s aldehyde oxidase (AO) reaction phenotyping assay determines if your compound is a substrate for aldehyde oxidase (AO).
Protocol
Aldehyde Oxidase (AO) Reaction Phenotyping Assay Protocol
Data
Data from the Aldehyde Oxidase (AO) Reaction Phenotyping Assay
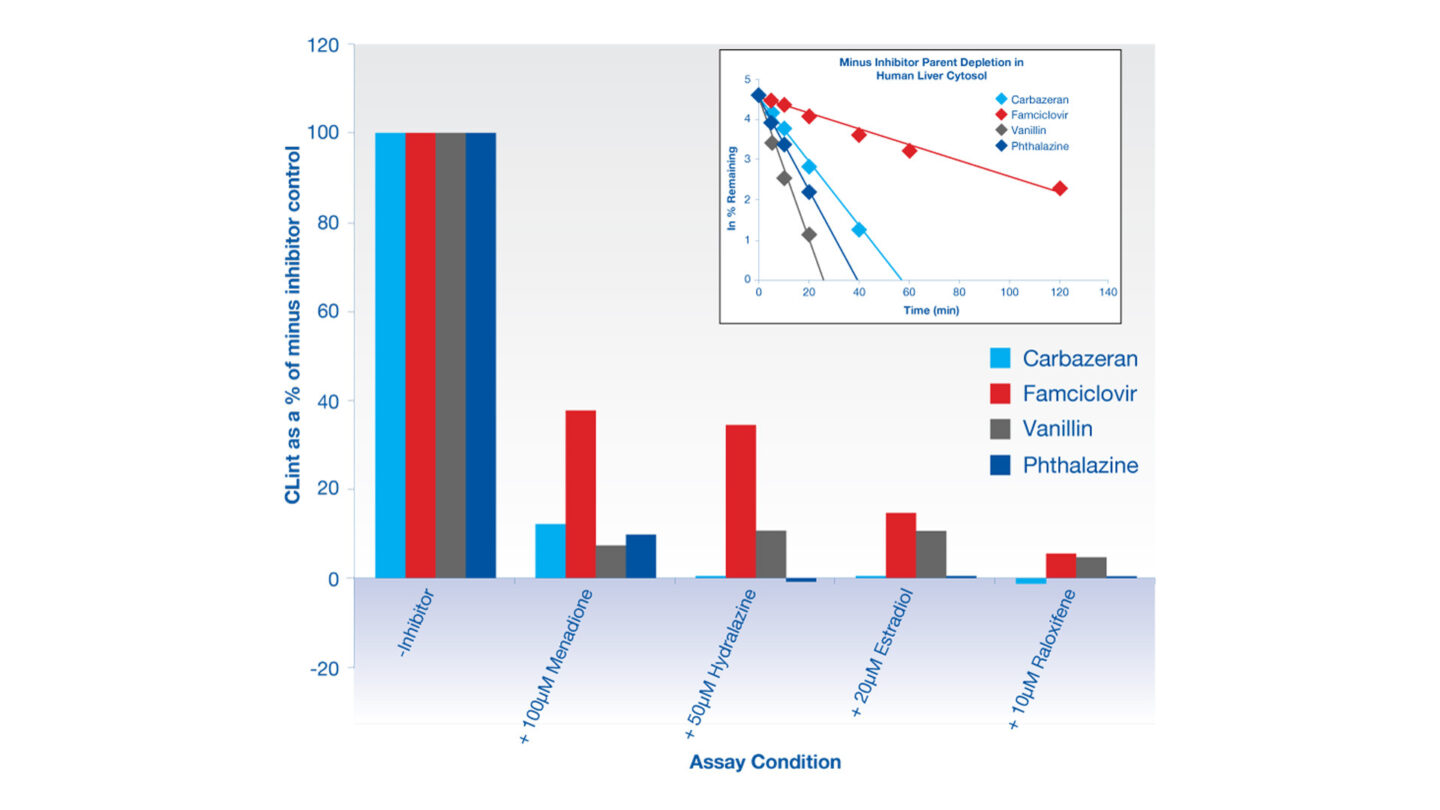
Figure 1
Results from human liver cytosol stability of AO substrates carbazeran, famciclovir, vanillin and phthalazine in the presence of different AO inhibitors, displayed as a percentage of the CLint of the minus inhibitor control compound. Inset: displays substrate depletion over time in the absence of inhibitor.
Downloads
- Cyprotex ADME Guide 5th Edition >
- Cyprotex DDI Regulatory Guide 3rd Edition >
- Cyprotex Aldehyde Oxidase Reaction Phenotyping Factsheet >